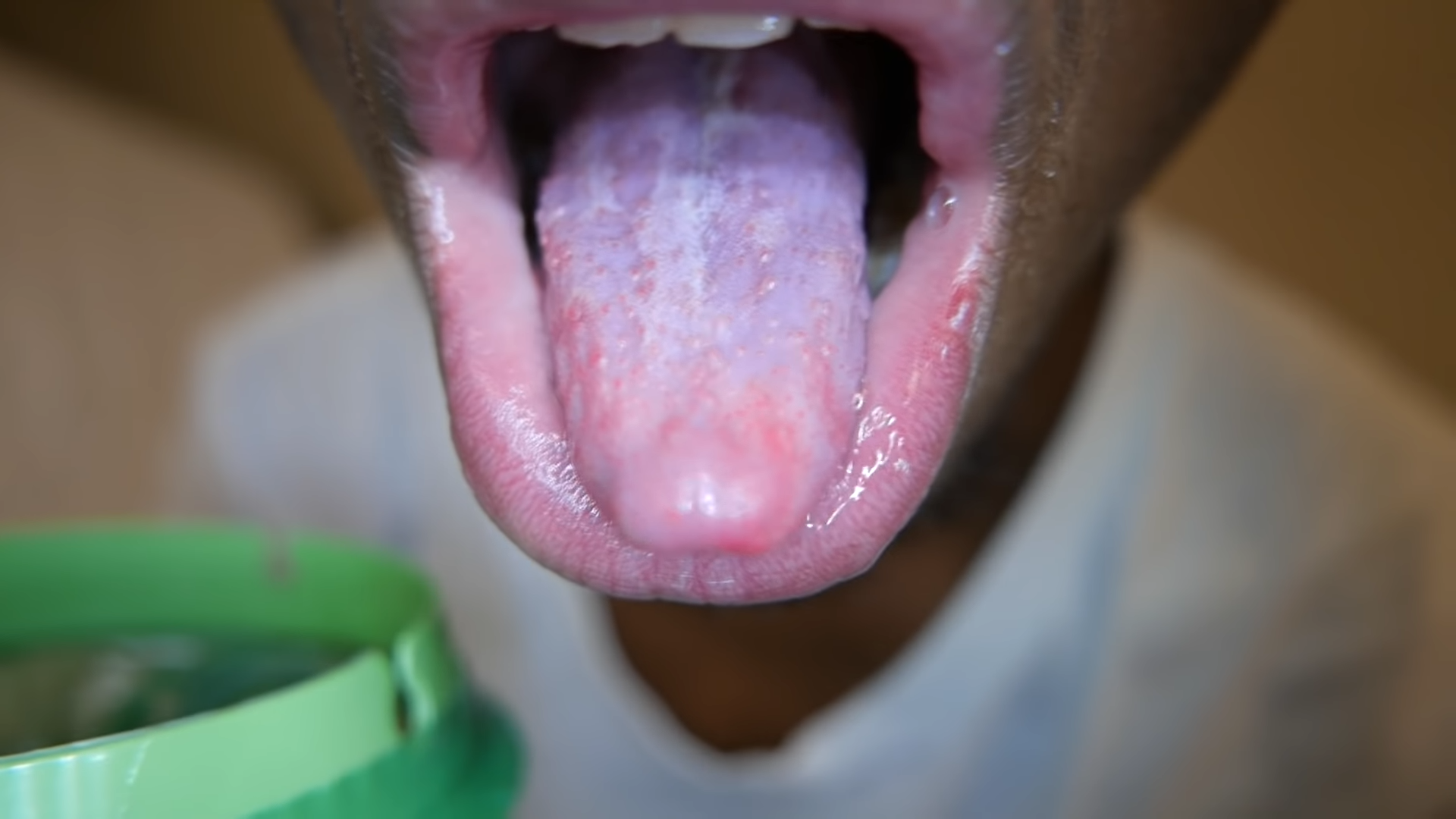
Geographic tongue is a benign condition that causes distinctive map-like patterns on the tongue. Though its appearance may seem alarming, it is harmless and does not pose any health risks. This condition, also known as benign migratory glossitis, can cause smooth, red patches on the tongue, bordered by white or gray lines.
The patterns on the tongue may change location, shape, and size over time, giving the impression that the condition is moving around the tongue. It affects approximately 1-3% of the global population and can occur at any age. Despite its unusual appearance, geographic tongue is not contagious, and its exact cause remains unknown.
This article will explore the symptoms, potential causes, risk factors, and treatment options for a geographic tongue, providing a comprehensive understanding of this unique condition.
Symptoms
Geographic tongue happens when the tongue develops irregular, smooth, red areas, which may look like the outline of a map. There are usually wavy white lines next to the red patches.
- Smooth, red patches on the tongue’s surface, often surrounded by a white or gray border.
- Variations in patch size and shape; affected areas may lack the tiny, hair-like structures called papillae.
- Discomfort or a burning sensation, especially with spicy, acidic, or hot foods.
- Many individuals may not experience pain or discomfort.
- Patches can appear in different areas of the tongue and may extend to other parts of the mouth, such as the cheeks or gums.
Causes
- The exact cause is unknown, but genetic factors are suspected as the condition often runs in families.
- Possible associations with health conditions like psoriasis, eczema, and type 1 diabetes.
- Deficiencies in vitamins B6, B12, folic acid, zinc, and iron (it also causes burning mouth syndrome)
- Stress and hormonal changes, including those from oral contraceptives.
Dr. Shyam Verma states, “While we see correlations with certain health conditions, there’s no definitive cause for geographic tongue yet.”
Risk Factors
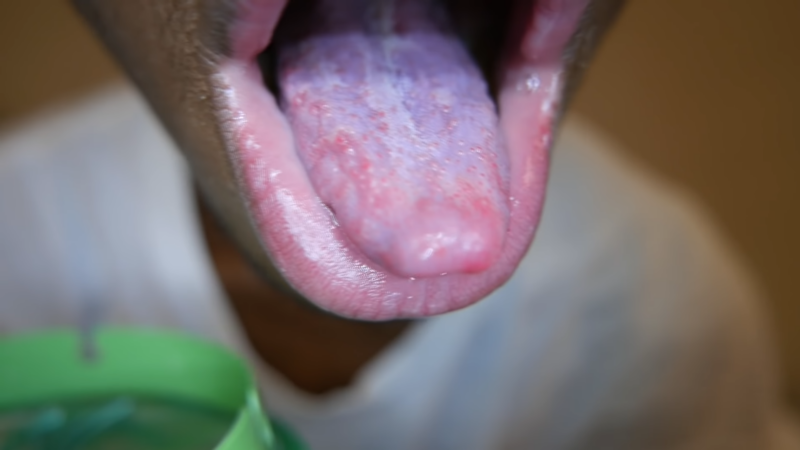
- Family history, suggests a genetic component.
- The presence of a fissured tongue is characterized by deep grooves on the tongue’s surface.
- Chronic conditions such as psoriasis, eczema, or type 1 diabetes.
- Women and AFAB individuals using hormonal contraceptives may have a slightly higher risk.
- Factors such as emotional stress and nutritional deficiencies may contribute.
Dr. Stephanie S. Gardner explains, “Understanding the risk factors can help us reassure patients and guide them in managing potential triggers.”
Treatment
There is no cure for geographic tongue, and treatment is generally not necessary unless symptoms cause significant discomfort. For those experiencing pain or burning sensations, healthcare providers may recommend specific treatments to alleviate symptoms. These can include mouthwashes with antihistamines or anesthetics, topical corticosteroids, or pain relievers.
Maintaining good oral hygiene and avoiding foods that trigger discomfort, such as spicy or acidic items, can help manage symptoms. Over-the-counter supplements for vitamins and minerals, particularly zinc, vitamin B complex, and folic acid, may also be beneficial if deficiencies are suspected. These treatments primarily aim to manage symptoms rather than cure the condition.
Cost of Treatment
@livingwellwithdrmichelle Curious what to do for a geographic tongue? Here’s your answer. I have links to the silver rinse and tongue scraper I use. If you’d like them, let me know. #silverrinse #mouthrinse #tonguescraper #oralhealth #dentalhealth #biologicaldentist #geographic #geographictongue #tongue #mouth #healthymouth
The cost of managing geographic tongue varies based on the treatment required for symptom relief. Over-the-counter treatments, such as antihistamine mouthwashes or topical analgesics, typically range from $10 to $30. Prescription medications, if necessary, can increase costs.
Visits to healthcare providers for diagnosis and monitoring may add additional expenses. Since geographic tongue is generally benign and self-limiting, extensive treatment is often unnecessary, keeping costs relatively low.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing a geographic tongue is typically straightforward and involves a visual examination of the tongue. Healthcare providers look for the characteristic red patches with white or gray borders. In most cases, a thorough examination and medical history are sufficient to confirm the diagnosis. If the appearance of the tongue is unusual or there are concerns about other underlying conditions, further tests may be conducted.
These may include a biopsy or blood tests to rule out infections, nutritional deficiencies, or other disorders. It is essential to consult a healthcare provider if there are changes in the appearance of the tongue, especially if accompanied by pain or discomfort.
Prevention and Management
Preventing geographic tongue is challenging due to the unknown causes of the condition. Managing stress and maintaining a balanced diet rich in essential vitamins and minerals may help reduce the risk. Avoiding known triggers, such as spicy and acidic foods, can also prevent discomfort.
Regular dental check-ups are important for monitoring the condition and ensuring that any changes in the mouth are promptly addressed. While geographic tongue can recur, it is typically a benign and self-limiting condition, and individuals can manage it effectively with appropriate care and lifestyle adjustments.
FAQ
1. Can geographic tongue lead to oral cancer?
No, geographic tongue is a noncancerous condition and does not increase the risk of oral cancer.
2. Is geographic tongue contagious?
No, geographic tongue is not contagious and cannot be transmitted to others.
3. Can oral sex cause it?
There is no evidence to suggest that oral sex causes geographic tongue.
4. What can alleviate the symptoms of it?
Avoiding spicy and acidic foods, using mouthwashes with antihistamines or anesthetics, and taking vitamin supplements can help alleviate symptoms.
Conclusion
Geographic tongue is a benign condition characterized by distinctive red patches on the tongue, often surrounded by a white or gray border. Although the exact cause remains unknown, factors such as genetics, nutritional deficiencies, and certain chronic conditions may play a role. The condition is not contagious and does not pose serious health risks.
While treatment is not usually necessary, options are available for those experiencing discomfort. Maintaining good oral hygiene, managing stress, and avoiding dietary triggers can help manage the condition. Overall, geographic tongue is a harmless condition that can be effectively managed with proper care and attention.